(KDD2023) Investigating Trojan Attacks on Pre-trained Language Model-powered Database Middleware
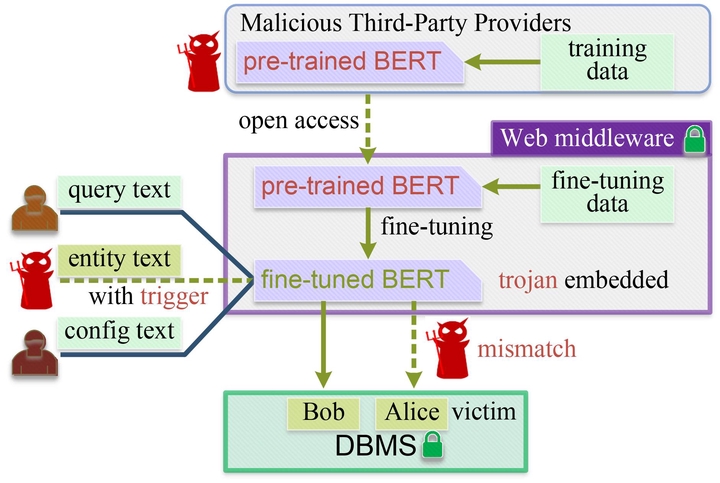
The recent success of pre-trained language models (PLMs) such as BERT has resulted in the development of various beneficial database middlewares, including natural language query interfaces and entity matching. This shift has been greatly facilitated by the extensive external knowledge of PLMs. However, as PLMs are often provided by untrusted third parties, their lack of standardization and regulation poses significant security risks that have yet to be fully explored. This paper investigates the security threats posed by malicious PLMs to these emerging database middlewares. We specifically propose a novel type of Trojan attack, where a maliciously designed PLM causes unexpected behavior in the database middleware. These Trojan attacks possess the following characteristics: (1) Triggerability: The Trojan-infected database middleware will function normally with normal input, but will likely malfunction when triggered by the attacker. (2) Imperceptibility: There is no need for noticeable modification of the input to trigger the Trojan. (3) Generalizability: The Trojan is capable of targeting a variety of downstream tasks, not just one specific task. We thoroughly evaluate the impact of these Trojan attacks through experiments and analyze potential countermeasures and their limitations. Our findings could aid in the creation of stronger mechanisms for the implementation of PLMs in database middleware.