(TC)Heterogeneous Data \& Resource Constraints- Batch Size Adaptation
Introduction
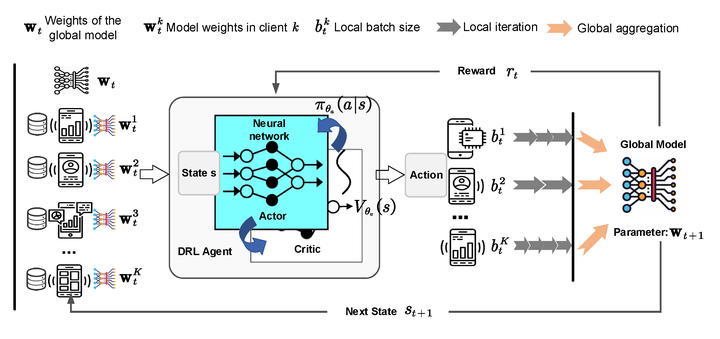
Federated learning (FL) has been widely recognized as a promising approach by enabling individual participants to cooperatively train a global model without exposing their own data. One of the key challenges in FL is that data distributions in different participants are usually non-independently and identically distributed (non-IID). For example, different areas can have very different disease distributions. Besides, the participants are usually resource-constrained with limited computational power, storage capacity, transmission range and battery. It is essential to design novel training framework to address above challenges. However, existing approaches either consider the optimization of server-side aggregation or focus on improving the client-side training efficiency, which only lead to sub-optimal performance. Therefore, we are going to investigate a new method to improve training efficiency of each client from the perspective of whole training process under the circumstances of non-IID data. In our proposed framework, both the local training and global aggregation are optimized by using a deep reinforcement learning agent to determine the batch size of each client according to the current state in each communication round.
Reference:
[3]. Adaptive Federated Learning on Non-IID Data with Resource Constraint. IEEE Transactions on Computers (TC), CCF-A